
BLOG

BLOG
Considering the massive amount of medical and healthcare records being generated across multiple institutions, the EHR plays an integral role in connecting all of them to provide real-time data of patients at a common platform.
Electronic Health Records ( EHR ) is the digitized collection of patients or populations' medical or health information. The vital health records of people are entered electronically by the healthcare providers throughout his/her lifetime. EHRs aim towards making the patient-centered records securely and instantly available to authorized users on demand. EHRs form an immensely vital part of health IT as it encompasses all advanced treatment histories of patients:
Table of Contents |
The Government of India aims to introduce a uniform maintenance system of Electronic Medical Records / Electronic Health Records (EMR / EHR ) by the healthcare providers and hospitals across the nation. The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare first initiated the standards for Electronic Health Record (EHR) for India back in September 2013. These pointers were on the basis of the recommendations made by the EMR Standards Committee constituted under the MoH&FW.
The draft of the EHR/ EMR Standards was hosted on the website of the Ministry initially, soliciting comments from the general public and stakeholders before implementation. After considering all the recommendations - the ‘EHR was finally passed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
With the rise of medical homecare devices and systems, meaningful healthcare data gets generated 24x7, which has long-term clinical relevance. This is where Electronic Health Record comes to the rescue as it collects all medical records generated during any clinical encounter or events.
Broadly, the goals of EHR can be defined as below:
The benefits of EHR can be defined as below:

Implementing an electronic health record is not a very easy process, as it can get very challenging if not carefully undertaken using a step-by-step approach.
And this step by step approach is guided by six significant steps:
Assess the Organization's Readiness: The preliminary step towards EHR implementation is to rightly assess the organization's current needs, goals, along with its financial and technical readiness towards the change. And, only post having an accurate view of the preparedness can the organizations design an EHR implementation plan which matches the specific organizational needs.
Plan the Adoption Approach: In the planning phase, organizations need to draw on the information gathered by them during the assessment stage in order to elaborately outline their EHR implementation plan. It's essential to measure and view each minute aspect of the plan from an electronic point-of-view.
Upgrade to or Select a Certified EHR: Next, organizations should upgrade to or select a certified and trusted EHR. The EHR implementation team should leverage the information gathered in the planning and assessment phases to choose the perfect EHR matching the organization's needs and challenges.
Conduct Training for Effective Implementation of an EHR System: During this phase of EHR implementation, organizations need to focus on training to ensure the successful migration to electronic data maintenance. They will also need to assure that they prepare for EHR implementation go-live, including training, pre-go-live dress rehearsals, along with elaborate pilot testing in this step.
Achieve Meaningful Use: Next, organizations should work towards achieving meaningful use, focusing on the shift towards the Merit-based incentive payment system.
The introduction of MACRA (the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act), brought in the Medicare EHR Incentive Program, which implies meaningful use. This later got transitioned to become one of the top four components of the latest Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS), which itself is part of MACRA.
MIPS harmonizes the existing CMS quality programs, the Physician Quality Reporting System, along with the Value-Based Payment Modifiers. MIPS combines multiple, quality programs into a single program to enhance quality care.
Continue Quality Improvement: Once enterprises have implemented an EHR and achieved its desired meaningful use, they should focus on continuous evaluation and improvement. It is critical to revisit the organization's goals and needs to refine the workflows and improve patient outcomes continuously.
Good read- Data Privacy and Security Risks In Healthcare Industry
Compared to paper medical records, threats to electronic health records security will no doubt be a hurdle to the efficient sharing of medical records within organizations. But, to optimize its benefits, there are major issues in electronic health records that organizations need to consider and overcome:
The use of EHRs has multiple benefits to healthcare organizations. But, those advantages remain linked to the data interoperability of the systems. When medical records are retrieved or saved, various aspects of the records are involved. And, the lack of interoperability solutions and standards has been a significant obstacle in the exchange of healthcare data between multiple stakeholders.
The data must be compatible with all organizations to maximize the benefits of EHRs to serve patients or even for research purposes. When authorized organizations or people receive and send medical records, the records need to be compatible even though they use diverse systems.
Organisations need to have a well-informed sense of assurance that the information risks and controls are balanced out. EHR systems may have multiple security vulnerabilities, and one of the biggest threats for EHR systems is malicious code. Software and hardware vulnerabilities removal is a must so that controls and risks are balanced to protect the system for effective business continuity.
EHRs involve sensitive, accurate, and confidential personal information of patients, like doctor's notes, prescription information, lab diagnosis, and personal and insurance-related information, which are too risky to be compromised. Medical records remain a lucrative target for hackers to commit cyber-crimes, including - identity thefts, phishing attacks, encryption blind spots, cloud threats, malware, and ransomware attacks. Hence, organisations need to prioritise cyber protection.
Business continuity planning (BCP) is essential to create strategies for maintaining continuous business operations before, during, and after disaster events. Network failure, hardware failure, data loss, software failure, and attacks are some easy examples of disruptions on EHR availability.
For the business continuity, EHRs must always be available over the network. To ensure network availability, BCP needs to be in place. Using the electronic format of health records can be challenging without immediate technical support from the in house IT staff. Digital data is prone to damage by malicious code, and hospitals may lose access to EHRs, so having effective BCP in place is a must.
This term defines the gap between people who have or who lack the access and know-how to technologies. The digital divide will leave many patients behind as they will not be able to derive the full benefits or services of the EHRs. This problem escalated in developing countries as EHRs are often not available.
Regardless of the availability of network infrastructure, few people are not familiar with computers and the Internet - the problem is grave in this case as well. Lack of skill, infrastructure, and knowledge remains the top hurdle behind the adoption of EHR.
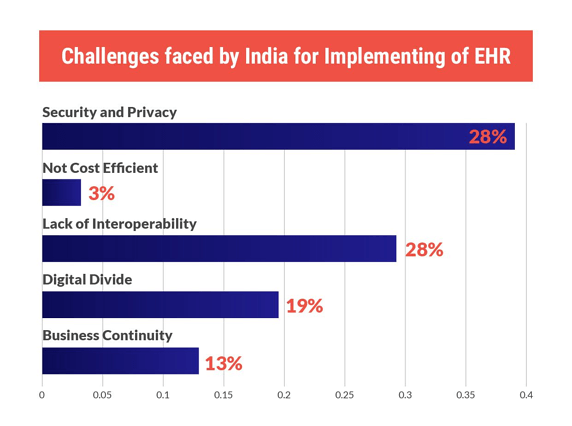
The development and implementation of EHRs involve lots of challenges. And, especially considering the Indian healthcare industry, the top challenges are:
To conclude, the implementation and development of Electronic Health Records in India are still at a very nascent but fragmented stage. It is crucial to focus on the following major issues in the electronic health record to succeed on the scale:
Once these primary issues get resolved, organisations will effectively move forward to a robust system of electronic health records available in real-time universally just a click away.
