
BLOG

BLOG
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks pose a significant threat to mobile applications, compromising user data and application integrity. This guide delves into the intricacies of MITM attacks on mobile apps, offering insights into detection methods and effective prevention strategies.
Businesses have long known that there are always weak links in security, especially mobile security. The worst part is not that companies get affected by these security issues but that public awareness is terribly low on how vulnerable this can be. The man-in-the-middle attack has been one of the most exploited ways hackers have tried and managed to steal information and money.
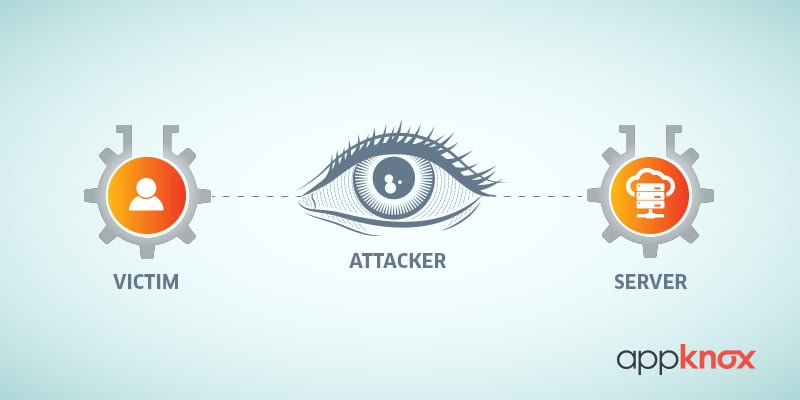
When an attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other, it is called a man-in-the-middle attack.
In simple words, a third person tries to break a connection between two people without them realizing this and is thus able to sniff and retrieve communication between them.
Public WiFi networks have been the best medium for hackers to perform man-in-the-middle attacks. Recently, the frequency and severity of such attacks have steeply increased. Simply put, by listening in and intercepting a mobile device's traffic, hackers can access the data flowing to and from the device and, hence, gather sensitive information.
So, if employees are careless about the information or data on their devices in public Wi-Fi networks, the scope of MitM attacks increases. This becomes even scarier if their personal and work devices are the same.
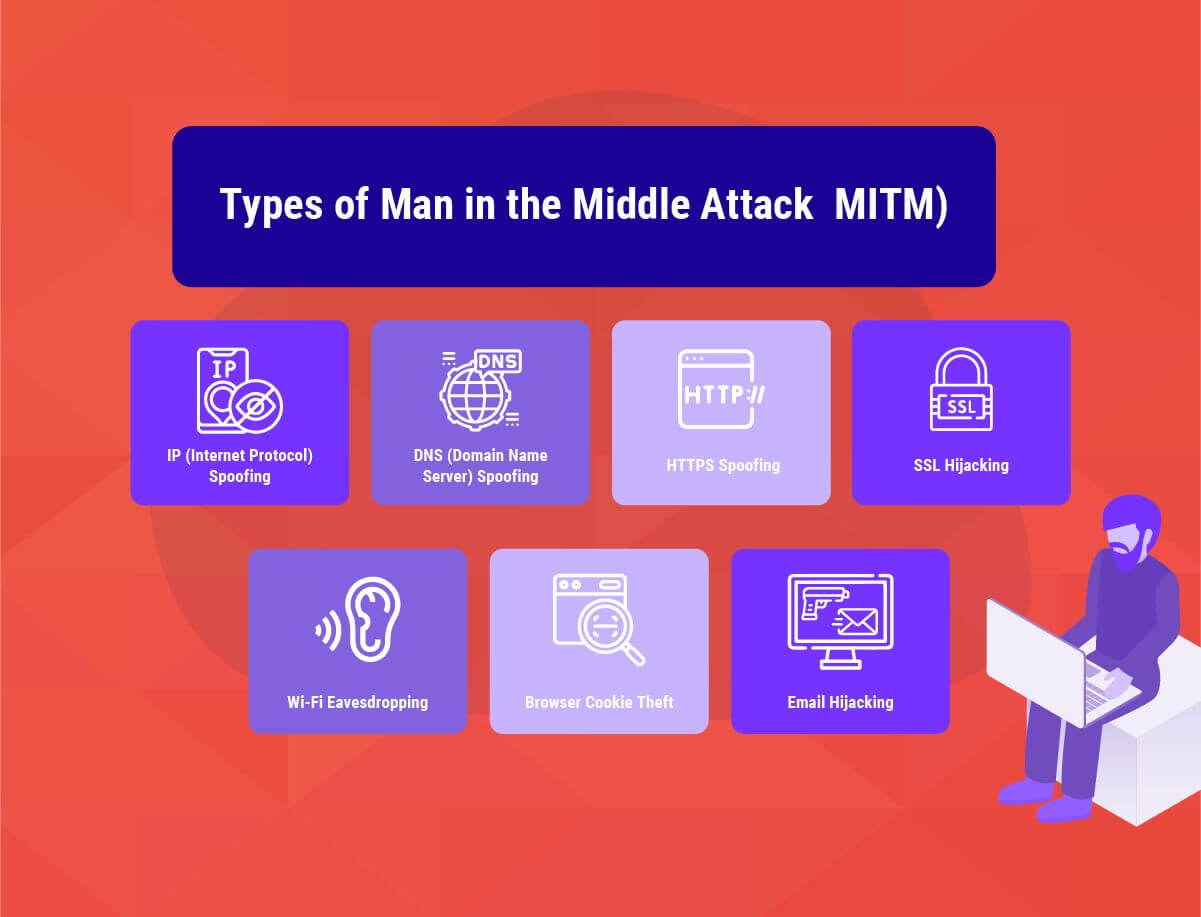
Cybercriminals utilize a variety of MITM attacks to gain control of sensitive networks and devices. The major types of MITM attacks include:
Similar to the address of our homes, every device that can connect to the Internet has an Internet protocol address (IP address) assigned to it. Attackers spoof IP addresses and trick users into thinking they are interacting with a genuine website or person over the Internet (which they are not), stealing sensitive information that the user would not have shared otherwise.
In the case of DNS spoofing, users are forced to unknowingly use a fake website created by the attacker rather than the original one they were trying to visit. Victims of DNS spoofing may think that they are visiting a trusted and safe website when, in fact, they are on a fake one and interacting with a threat actor.
The goal of the man-in-the-middle here is to divert the traffic from the real website to the fake one and gain access to user login credentials.
HTTPS in the URL is generally a bold sign of security and trust. But this doesn't mean the attackers leave no stone unturned for HTTPS domains. In HTTPS spoofing attacks, the hackers use domains that look similar to the original domain, with a slight difference in the non-ASCII characters. Users generally fall for this and are redirected to an insecure domain where the attackers monitor all their interactions.
SSL, or the Secure Sockets Layer, is a security protocol that establishes secure and encrypted links between the web server and your browser.
In the case of SSL hijacking, the attackers unencrypt the communication between the web server and client to be able to stage an MITM attack. In the process, the threat actors intercept all the secure information communicated between the client (user's browser or application) and the server.
In many cases, the threat actors target the email accounts of organizations, especially financial institutions, and use that to target their customers. The attackers then send their instructions to the customers by spoofing the organization's email addresses. The users are convinced to follow the instructions sent by the attackers, unwillingly share sensitive financial information, and even engage in fraudulent transactions.
Cybercriminals generally set up fake Wi-Fi connections that sound familiar to the users, sometimes similar to the names of their home Wi-Fi or a nearby business. Once the users onboard such Wi-Fi connections, the attackers can track the users' online activity and gain access to their login info, payment-related information, and much more.
These Wi-Fi connections are usually public and require no user authentication.
Websites store browser cookies that contain a small amount of information about your online activity on your computer.
For example, an e-commerce website might store information related to your past purchases, cart additions, and login information so that you don't have to re-enter it once you revisit the website. In several cases, attackers hijack these cookies to access your passwords, addresses, and other sensitive data.
Data in transit and traveling across your mobile device and servers goes to places beyond your imagination. So, is it safe, and can we be sure that nobody can sniff the sensitive personal information we share with several apps and services we use?
The data generated from our mobile devices is transmitted over the WiFi network or the mobile connection to the operator's base transceiver station (also known as BTS). Then, the data is redirected several times to several receiving stations.
During its journey, the data is assessed by several automated agents, such as antivirus and antispam appliances. In every such instance, when the data is even under someone's supervision, it is possible that someone could illegally eavesdrop on it and access information you would never wish to share with someone.
The man-in-the-middle attack is not new. It has been around for a few years but is mainly restricted to computers and laptops.
With mobile growing at a lightning pace, there has been a shift in emphasis to hacking mobile devices. This is particularly worrying as it gives access to a lot of information, like personal identity, location, and messages. Hackers can also eavesdrop on conversations.
Mobile apps must communicate with remote servers to function, and most use HTTPS to do so securely. However, problems arise when apps fail to use standard authentication methods properly. Some, for example, don’t reliably check the certificate that proves a server is what it says it is. Others fail to verify their server’s hostname properly.
To be secure, mobile apps must validate the hostname, ensure the certificate matches the server’s hostname, and ensure a valid root authority trusts the certificate.
Despite various techniques, almost all MITM attacks have a straightforward execution order. These attacks can generally be divided into three operational stages.
In the first stage, the attacker obtains access to the location from which he can execute the attack.
In the second stage, the attacker becomes the man in the middle by intercepting the peer-to-peer communication.
In the third and final stage, they overcome any existing encryption to steal information.
The MITM attackers sit between the established connections of two parties to manipulate or observe the ongoing traffic. They can do this either by manipulating existing legitimate networks or creating completely fake replicas of the network with the attackers themselves in control. Then, they dismantle any encryption on the compromised traffic and change or reroute it to a destination of their own choice.
Attackers often silently re-encrypt the compromised traffic to their target or simply observe it, making MITM a tough attack to identify.
A common perception is that MITM attacks are fairly easy to execute. WiFi traffic is generally broadcast in the open, so any device nearby can sniff your data traffic.
The job becomes even easier if someone uses unencrypted or public WiFi and connects to some web page via HTTP. Attackers commonly use technologies like Aircrack-ng and WiFi pineapples to lure users into their open WiFi networks and perform an MITM attack easily.
Hundreds of automated tools and online tutorials are available on the Internet, especially on YouTube, which suggests that anyone could easily do it.
Simply put, everyone in the mobile enterprise is a potential target, but the most vulnerable are those in senior or executive positions in business and government. It is obvious that hackers look out for people who are important or have access to sensitive information.
Nowadays, since most businesses have started allowing employees to use their devices at work, this threat impacts everyone almost equally. More often than not, it is easier to access a network through a device you think has the least probability of getting hacked.
The problem is genuine and severe.
More than 75% of the apps on the Google Play store do not meet basic security checks. Before you think you are safe on iOS, let me tell you that iOS is equally prone to such attacks.
Preventing MITM attacks requires several small but practical steps on the part of users and a combination of verification and encryption methods on the part of the application and web developers.
Users can play their part by avoiding connecting to Wi-Fi networks that are not password-protected. Users should avoid using public networks while doing sensitive transactions like bank transfers or logins. Paying close attention to the notifications your browser sends when it flags some websites as unsecured and logging out of applications when not in use can also go a long way.
For developers, it becomes essential to implement secure communication protocols like HTTPS and TLS. These protocols help mitigate hijacking and spoofing attacks by authenticating and encrypting data in transit. This practice prevents the decryption of sensitive data like authentication tokens and avoids the interception of site traffic.
Application developers should also use SSL/TLS and strengthen the security of each page rather than just focusing on the pages that require login credentials from users. This massively reduces the chances of a hacker stealing session cookies when a user is browsing an unprotected section of the website or the application while logged in.
Man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM) pose a grave threat to web or mobile application security. If protection measures are not in place, these attacks are easy to execute and difficult to detect, and they reward the attackers with access to a plethora of sensitive user and business-related information.
Given the level of damage these attacks can cause, it becomes critical for business stakeholders to understand and identify their underlying vulnerabilities and implement all the preventive measures to keep their infrastructure safe and secure from these attacks.
.jpg?width=50&height=50&name=10606600_10204086667262761_7381430219125488912_n%20(1).jpg)