
BLOG

BLOG
Mobile payments are transforming transactions, but they also introduce security risks. One primary concern is mobile payment bypass—a technique hackers use to evade payment authentication and exploit system loopholes.
Understanding these threats is critical for CISOs, CXOs, security leaders, and developers. This blog dives into how mobile payment bypass works, real-world risks, and essential strategies to safeguard your payment infrastructure.
Payment bypass is a type of parameter tampering attack where the manipulation of parameters exchanged between client and server is done to modify application data, such as user price, the quantity of product, etc.
Imagine buying a Biryani of Rs.200 by paying Rs 2, doing a mobile recharge worth Rs.349 by just paying Re.1, or buying all your cosmetic products for free. Mind-boggling, right?
But these are all possible with just a few steps. It’s a fortunate stroke of serendipity for the user but a substantial financial loss for the business owners.
We thought of checking out the issue in 10 e-commerce apps in India, and it was shocking to see that 8 of them were vulnerable to payment bypass attacks.
There are five types of mobile payments:
1. Mobile wallets – Apps like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay store card details for quick tap-to-pay transactions.
2. QR code payments – Users scan a QR code to pay, commonly used in apps like PayPal, WeChat Pay, and Alipay.
3. NFC (Near Field Communication) payments – Contactless payments using NFC-enabled devices, often integrated into mobile wallets.
4. Direct carrier billing – Charges are added directly to a user's mobile phone bill, often used for digital purchases.
5. Mobile bank transfers & P2P payments – Apps like Venmo, Zelle, and Revolut enable instant peer-to-peer money transfers.
Most companies are developing their mobile apps and integrating payment features to ease the transaction process for consumers.
Whether it’s an e-commerce, travel, or food app, mobile payment significantly boosts a company's sales. Besides getting attention from the users, it also brings many malicious users to exploit the system.
|
Did you know the first mobile payment was made in 1997 when Coca-Cola introduced SMS purchasing? Exxon Mobile began accepting contactless payments using Speedpass in the same year. Since then, mobile payments have evolved significantly, and today, payments are made via Bluetooth and NFC. |
There are many ways of doing it, but one of the most commonly used methods is tampering with the request/response from the app/server using any proxy tool (BurpSuite, Tamperdata, etc.)
Essentially, there are three simple steps to checking if your mobile app can be exploited by payment bypass.
1. Configure the BurpSuite with your system and install the mobile app where you want to test it. You may follow this link to set up.
2. Log in to the mobile app, select your products, and add them to the cart.
3. The magic begins before you check out. We need to turn the “intercept on” in the Burpsuite, and we can see the price is being sent as a query string in the request. All we need to do is change the Rs.400 to Rs.10. The server relies on the input provided by the user and accepts the value of 10 for the products. The query gets processed, and the success message is displayed to the user.
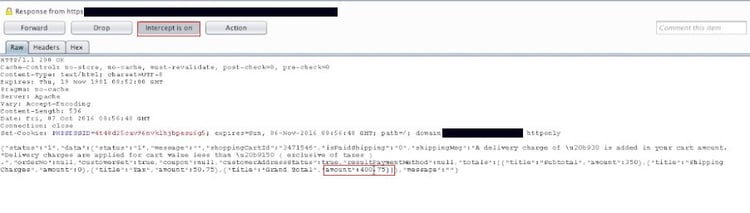
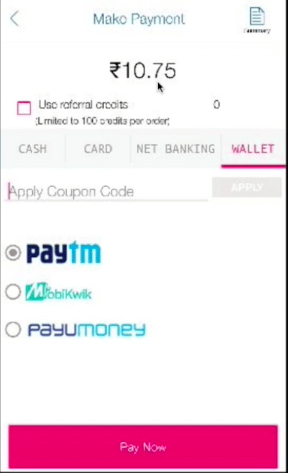
Most developers mainly focus on features and functionalities but completely lack security implementation.
They generally think that payment gateways take care of the security, but it's not secure if a proper implementation is not done. Most payment gateways are safe and handle multiple levels of checks, but without proper integration with the mobile app, it’s as useless as the fifth wheel.
This is probably one of the most critical issues since it directly impacts the company's revenue and leads to financial loss. Few companies even had to remove the online payment integration feature and convert it to only “cash on delivery.”
It’s not as difficult as it seems to protect the system from payment bypass. All you need to do is to follow a few simple guidelines and implement them properly.
Level 1 - It is recommended that sensitive or unnecessary parameters be removed.
Level 2 - The price (parameters) should be validated on the server side. It also should use protections like cryptographic checksums. When tampered with, the server should not process the request.
Level 3 - Apart from this, you may build a system with anomalies to detect these unusual transactions automatically. At least, such orders are not processed even after successful payment.
There are almost 4-5 modes of payment in any mobile app, such as credit card, debit card, net banking, wallets, UPI, etc. As we know, the payment gateway already takes care of security at certain levels.
However, out of all the above payment modes, net banking is the favorite attack vector for hackers. This is because the checksum is handled by the payment gateway and the merchant, not by VISA or MasterCard.
A credit card is more mature for merchant payments. Banks are more towards account beneficiary transfers. With the net-banking mode, different banks have different modes of checks, there is no unified standard.
On the other hand, UPI is revolutionary, as it follows one standard across all the banks. Since the difference in standards for each bank to integrate net-banking options across all the banks requires much work from the developer side, the attacker has a surface large enough to explore.
Mobile payments are steering us toward a cashless economy where payments can be made in a blink of an eye. But, before that can happen, these fundamental security issues discussed above must be addressed.
We are witnessing the exponential growth of mobile payments across the globe. People don’t think much of making expensive purchases like flight tickets or paying bills via mobile. However, security is something that always has to run parallel with innovation.

Hackers never rest. Neither should your security!
Stay ahead of emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices in mobile app security—delivered straight to your inbox.
![]() Exclusive insights. Zero fluff. Absolute security.
Exclusive insights. Zero fluff. Absolute security.
![]() Join the Appknox Security Insider Newsletter!
Join the Appknox Security Insider Newsletter!
