
BLOG

BLOG
Vulnerability scanning is undoubtedly the go-to option for establishing a robust mobile application security posture. However, given the complex cybersecurity challenges of modern times, implementing vulnerability scanning properly might be complicated and challenging.
According to the 2020 Edgescan Vulnerability Statistics Report, around 35% of the vulnerabilities discovered in external-facing apps were critical or high risk. Given such levels of security risk, organizations must roll up their sleeves and turn to mature security practices like vulnerability scans to mitigate the underlying security risks and strengthen their security infrastructure.
Whether your organization is looking to improve its already mature security posture or striving to enhance the security of its applications, this is a must-read blog post.
Vulnerability scanning is an automated process of proactively assessing applications, networks, and other security infrastructure vulnerabilities. It is usually performed by third-party security service providers or the organization's IT department. However, security attackers who are keen on finding points of entry into an existing network may also perform vulnerability scans.
The vulnerability scanning process consists of classifying and detecting system vulnerabilities in communications equipment, networks, and computers. Apart from identifying security loopholes, vulnerability scanning also checks the countermeasures necessary to effectively prevent possible attacks.
Now, let’s talk about internal and external vulnerability scans and their importance for your security infrastructure.
Internal vulnerability scanning is performing a scan from a location that already has access to the system's internal network. These scans are mostly performed within the internal network environment. Contrary to external scans, internal vulnerability scans can see through the existing network for security vulnerabilities with greater depth.
Internal scans have several unique benefits. Taking a proactive approach to performing internal vulnerability scans helps protect the existing network from several known and unknown vulnerabilities. These types of scans work best when you need to verify that your patches have been implemented correctly or when you need to provide a detailed report regarding the existing vulnerabilities in the network for an in-depth analysis.
When performing internal vulnerability scans, you get two major options to choose from - credential and non-credentialed scans. Each of them plays an essential role in identifying the depth and level of risk the vulnerabilities pose.
Credential scans utilize admin accounts and perform detailed checks, focusing on vulnerabilities that can’t be seen from within the existing network. Non-credentialed scans, on the other hand, provide a brief view of the vulnerabilities by utilizing the existing networks hosted by the network host.
Although credential scans provide a deeper understanding of the existing vulnerabilities to an outsider (one who might attempt to exploit the known vulnerabilities via a phishing attempt or a malicious download), it is also important to understand that not all attacks come from the outside.
Some attacks may also come from within the firewall. Since technology is becoming readily available and viable for non-technical users, the risk posed by an inside attack becomes more vivid and real. The non-credentialed scans help prevent insider attacks by simulating what type of information a privileged insider has access to regarding the organization's security posture.
It might not sound that useful initially, but a non-credentialed scan should never be missed. It might be surprising for you to find out how much a regular insider can learn about your internal network infrastructure; with that information, they can do all sorts of damage.
External vulnerability scanning or perimeter scanning is performed from outside the existing network. These scans help identify vulnerabilities that threaten assets exposed to the outside world, such as the Internet. They are targeted at external IP addresses of your existing network.
You will find useful information from these scans, including potential vulnerabilities and a list of ports exposed openly to the Internet. External scans work best when you need to identify the strength of your externally facing services.
Must Read: Difference between Agent-based and Network-based Internal Vulnerability Scanning
Systems facing the internet are constantly being scanned for loopholes and attacked regularly. Even if you are not running those scans, someone else will, and you never know what intentions they have in mind. Attackers are always scanning unpatched systems to exploit vulnerabilities, and the global nature of the internet makes it even easier for them to carry on these attacks with utmost impunity.
Even if security patches exist within your system, attackers can utilize the lag time between identifying the vulnerability and implementing an associated security patch. That is why it becomes essential to run vulnerability scans that help reveal the missing patches that must be implemented on time.
The threat of hackers and malware isn’t present only outside of your firewall; it can also be present inside. While the basic idea of threats originating from the Internet is understood by many and makes sense to many people, what is often overlooked is the fact that these threats may originate from within the internal network as well.
These types of threats may include disgruntled employees who have been keen on targeting systems from the inside or malware (such as viruses or Trojans) downloaded via the Internet or a USB stick on a networked computer. When the malware enters the internal network, it looks out for other systems and services on the internal network as well.
This is why both internal and external vulnerability scans are required to identify significant vulnerabilities. While an external scan detects vulnerabilities outside the firewall, internal scans aim to detect vulnerabilities within the firewall. Running an internal scan enhances the security of your internal network and prevents threat actors who have established a foothold inside your network from gaining more privileges.
The major aim of vulnerability scans is to provide a feedback loop that can help enhance your organization's overall security posture. After each scan, it is important to review the applied patches and get the remediation efforts approved by the IT and security teams.
It is important to act quickly after completing the vulnerability scans. Often, these scans are followed up with little or no analysis of the next steps. A proper risk assessment must be performed in a way that makes sense to the organization, apart from minimizing the possibility of overlooking potential threats.
For all the organizational stakeholders, a specific tool called the vulnerability assessment risk matrix plays an important role in visually representing the scan results in an easily understandable format. The matrix may assist finance personnel, IT staff, security teams, operation stakeholders, and the executive leadership of the organization in security-specific decision-making.
Here’s a screenshot of the vulnerabilities detected in a test app, prioritized based on the CVSS score on a scale of 1- 10, with 10 being the highest severity and 1 being the lowest severity.
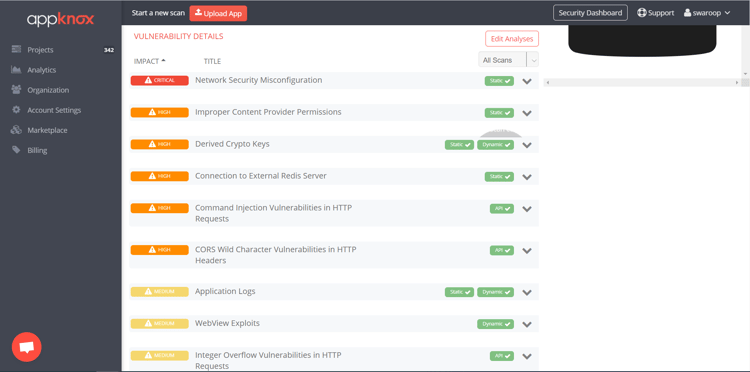
Although the number of medium and high vulnerabilities may be higher, you should also focus on reviewing the less critical and rare vulnerabilities.
When it comes to assessing your organization’s stance on security, vulnerability scans are the primary source of knowledge. These scans provide instant support while rebuilding and strengthening the security posture of your existing network. If you want to bolster your security defenses inside out, vulnerability scanning is surely the go-to process. Analysis and vulnerability scanning can go a long way in helping your organization fine-tune further security efforts, apart from providing you with one of the most decent returns on your security testing investment.
.jpg?width=50&height=50&name=10606600_10204086667262761_7381430219125488912_n%20(1).jpg)